The Universe
- Apr 6, 2018
- 2 min read
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT
Extremely large distances between objects in our solar system and universe call for the use of larger units of measure.
ASTRONOMICAL UNIT (AU) - the average distance between the Earth and the Sun
Astronomical Units are mostly useful for describing distances within our solar system. For example, we say that the distance between the Sun and Earth is 1AU. Mars orbits the Sun about 50% further out than Earth's orbit, so we say that the distance between the Sun and Mars is about 1.5AU. Neptune's orbit is more than 30 times larger than Earth's, so it is about 30.1AU from the Sun.
How Big is the Solar System?
LIGHT YEAR - the distance that light travels through space in one year (Earth-year). Note: Light years measure distance, not time!
Light years are mostly useful for describing distances between objects outside of our solar system, for example the distance between stars or galaxies. It takes light from the nearest star to our own solar system, Prixima Centauri, about 4.3 years to reach us. As a result, we say that Proxima Centauri is about 4.3 light years away. The distance from our Sun to the opposite side of our galaxy, the Milky Way, is about 52,000 light years. This means that when we look at a star on the far side of the galaxy, we are seeing light that has been travelling through space for 52,000 years. In other words, we are seeing what that star looked like 52,000 years ago!
SOLAR SYSTEMS, GALAXIES, and GALAXY CLUSTERS
Scientists have observed planets orbiting other stars, leading them to believe that solar systems such as ours are not a rare thing within the universe.
Stars tend to form in "clumps", called STAR CLUSTERS. These star clusters are part of a larger system of hundreds of billions of stars grouped together by gravity called GALAXIES.
Galaxies are classified by their shape, and include spiral galaxies (such as our own Milky Way), elliptical galaxies, and irregular galaxies.
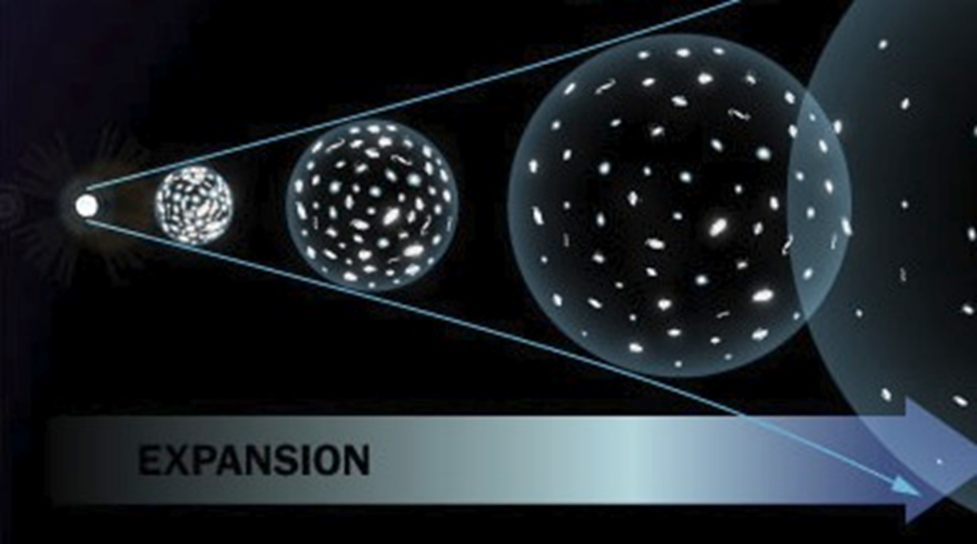
Like stars, galaxies tend to be clumped together in GALAXY CLUSTERS.
Scientists have observed that all galaxies appear to be moving away from each other, providing evidence that our universe is expanding! This supports what scientists have called the "big bang theory" as an explanation for the beginning of our universe.
How Many Stars are There?
Why is the Universe So Empty?




Comments